
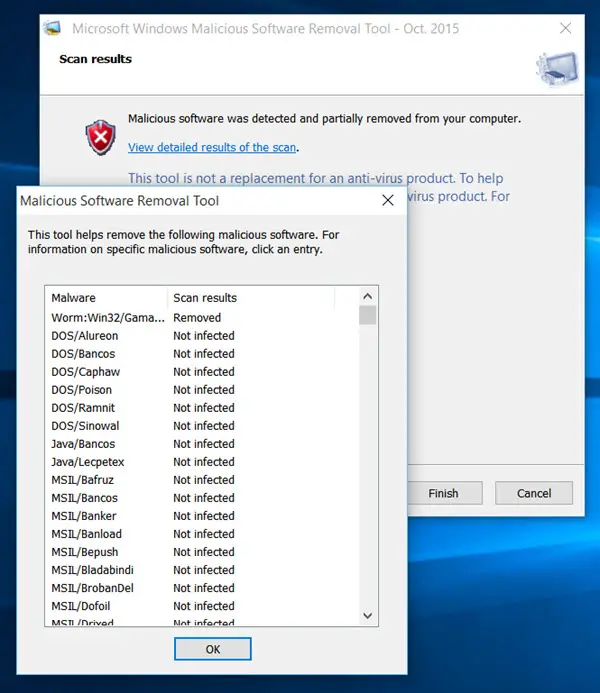
Starting with version 5.1, released on June 11, 2013, support for Windows 2000 was dropped altogether. The last version of the tool that could run on Windows 2000 was 4.20, released on May 14, 2013. Since support for Windows 2000 ended on July 13, 2010, Microsoft stopped distributing the tool to Windows 2000 users via Windows Update. The tool is also available as a standalone download. Microsoft releases the updated tool every second Tuesday of every month (commonly called " Patch Tuesday") through Windows Update, at which point it runs once automatically in the background and reports if malicious software is found. Approximately two million hosts had been cleaned by October although this was slightly less than half of the estimated infections, the rest of the suspected machines presumably did not have their automatic Windows Updates enabled or manually run.
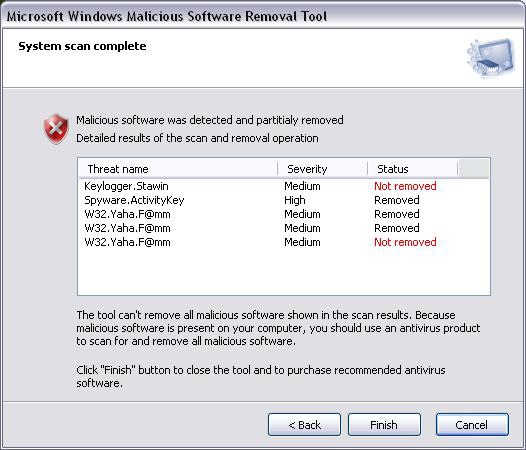
In August 2013, the Malicious Software Removal Tool deleted old, vulnerable versions of the Tor client to end the spread of the Sefnit botnet (which mined for bitcoins without the host owner's approval and later engaged in click fraud). On May 19, 2009, Microsoft claimed that the software has removed password stealer threats from 859,842 machines. The report also stated that, on average, the tool removes malicious software from 1 in every 311 computers on which it runs. In a June 2006 Microsoft report, the company claimed that the tool had removed 16 million instances of malicious software from 5.7 million of 270 million total unique Windows computers since its release in January 2005. The reporting behavior is disclosed in the tool's EULA, and can be disabled if desired. The tool is configured to report anonymized data about any detected infections to Microsoft. Windows+ R %windir%\system32\mrt.exe ↵ Enter To run it manually at other times, users can use the Windows Command Prompt or Run command via the Start Menu or the Windows + R key, and then start "mrt.exe". The tool records its results in a log file located at %windir%\debug\mrt.log.

It is automatically distributed to Microsoft Windows computers via the Windows Update service but can also be separately downloaded from the Microsoft Download Center. First released on January 13, 2005, it is an on-demand anti-virus tool ("on-demand" means it lacks real-time protection) that scans the computer for specific widespread malware and tries to eliminate the infection. Microsoft Windows Malicious Software Removal Tool is a freely distributed virus removal tool developed by Microsoft for the Microsoft Windows operating system. com /en-us /help /890830 /remove-specific-prevalent-malware-with-windows-malicious-software-remo English, Portuguese, Arabic, Chinese, Czech, Danish, Dutch, Finnish, French, German, Greek, Hebrew, Hungarian, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Norwegian, Polish, Portuguese, Russian, Spanish, Swedish and Turkish


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
